Abstract
Background: Primary CNS lymphoma (PCNSL) is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma that relies on chronic active B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling. Patients with chemo-refractory PCNSL or relapsed < 1y have a median OS of only 2-4 mos. Ibrutinib targets BCR signaling through inhibition of BTK. In a phase 1 study, we showed tumor reductions after a 14-day ibrutinib window in 94%, including complete remissions (CR) (Lionakis et al. Cancer Cell 2017). Further, ibrutinib added to anthracycline-based chemotherapy (DA-TEDDi-R) achieved CR in 86% of evaluable patients. Routine use of DA-TEDDi-R, however, is limited by our observation of 7 presumed or proven cases of Aspergillus when no fungal prophylaxis was given and in conjunction with high dose steroids. Herein, we report the durability of CR and PFS in relapsed/refractory patients with extended follow-up.
Methods: Patients with untreated or relapsed/refractory PCNSL, age >18, and adequate organ function were enrolled. Previous BTK inhibitor, EBV+, and active pregnancy were excluded. Patients had baseline MRI brain, PET/CT brain and body, Ommaya placed, CSF analysis with flow cytometry, and ophthamologic evaluation. A window of ibrutinib x 14d was given in 3 cohorts at escalating doses (560mg, 700mg, 840mg) then repeat MRI to assess activity. After ibrutinib window, patients received up to 6 cycles of ibrutinib + TEDD-R (temozolamide, etoposide, doxil, dexamethasone, rituximab) with ICV or IT cytarabine. No pt received maintenance or consolidation. All remissions by MRI were confirmed with PET/CT brain and repeat CSF analysis. Surveillance brain MRI after treatment q3mos for 1y, q4mos x 1y, q6mos x 1y, then annually.
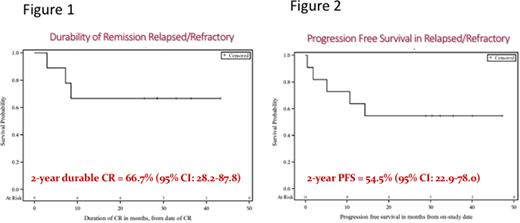
Results:18 PCNSL patients with a median age 66 (range 49-87) were enrolled between August 2014 and March 2016. 5 patients were untreated, 2 relapsed, and 11 chemo-refractory. After a median potential f/u of 38.9m, the median PFS for all patients who received DA-TEDDi-R is 15.2m (95% CI:3.8-undefined) and the 2-yr PFS is 43.8% (95% CI: 19.8-65.6). Of 13 relapsed/refractory patients, 2 died from Aspergillus infection during the ibrutinib window; neither had fungal prophylaxis and both had high-dose steroids. 11 patients received a median of 5 cycles (range 1-6) of DA-TEDDi-R. Nine (82%) of these patients achieved CR/CRu. Notably, none of the 6 patients with relapsed/refractory PCNSL (1 relapsed, 5 refractory) in CR at the time of publication have relapsed or died. The median duration of CR in relapsed/refractory PCNSL has not yet been reached (range 2-43m) and the 2-year durable CR rate is 66.7% (95% CI: 28.2-87.8) (Figure 1). Of the 11 relapsed/refractory patients who received DA-TEDDi-R, the median PFS has not yet been reached and the 2-yr PFS is 54.5% (95% CI: 22.9-78.0) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: Ibrutinib + anthracycline-based chemotherapy (TEDDi-R) induces durable complete remissions in PCNSL without maintenance or consolidation, including patients with disease refractory to chemotherapy. Risk of Aspergillus infections mandates use of fungal prophylaxis and judicious use of steroids. Phase 1 study of escalating ibrutinib doses with concurrent isavuconazole is currently enrolling patients with relapsed and refractory PCNSL (NCT02203526).
This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of NCI at NIH
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal